Analysis of Taxation System in UAE
The UAE’s dynamic economy, openness to international business and strategic location is definitely a gateway to the region. The United Arab Emirates is a federation of seven emirates, with autonomous emirates and local governments.The tax system and structure become the next important thing to know about UAE.
BACKGROUND OF TAXES IN UAEs
The thought of taxes begins with Corporate and Income taxes. The Income tax decrees have been issued in five of the seven Emirates in UAE, being – Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm Al Quwain, Ras Al Khaimah and Fujairah, but they are not currently enforced on most businesses. Hence resulting in no corporate taxation in most industries. However, the UAE leviescorporate tax on oil and gas exploration and production companies. Also, the branches of foreign banks are subject to income tax under separate banking tax decrees in certain Emirates (Eg. Dubai, Abu Dhabi).
At present, there are no tax laws that apply to individuals in the UAE. However, the Federal Tax Authority does issueTax Residence Certificates to individuals who satisfy the requirements specified by the Authority to take advantage of DTAA. The UAE concluded 115 DTA to with most of its trade partners.
UAE being a hub to international trade, Customs Duty needs its share of discussion. It takes generally, a customs duty of 5% – imposed on the cost, insurance, and freight (CIF) of value of imports. Other rates may apply to certain goods, such as alcohol and tobacco, and certain exemptions and reliefs may also be available.The United Arab Emirates is part of the GCC Customs Union, which was established in 2003 to remove customs and trade barriers among the GCC member states.
Certain industries such as hotel accommodation, leisure services etc.are subject toMunicipal Taxesare imposed in UAE. On property rentals, certain Emirates in UAE charge a municipality fee on the annual rental value of the property, based on the Emirate in which the property is situated.
In 2017, The European Union Commission published a black list of 17 countries, that have been failing to meet the agreed good tax governance standards which included UAE. UAE has committed to meet the minimum standards to walk shoulder to shoulder with G20 countries, and not get contaminated to any allegations of being tax haven or contributing to base erosion and profit shifting. Of the 15 Action Plans, UAE being the member of BEPS inclusive framework has to comply with 4 of those actions. Henceforth UAE was removed from the non-cooperative list and placed on watch list with effect from 10th October 2019.This has led the Economic Substance Regulationsto make its way to UAE, to come in line with UAE’s commitment to the international tax cooperation and transparency. UAE has also issued Cabinet of Ministers Resolution No.32 of 2019, setting forth the country-by-country reporting rules that are broadly in line with the guidance issued by the OECD.
Excise tax was also introduced across the UAE in 2017. The Federal Tax Authority in UAE pointed out that the application of Excise Tax laws achieved remarkable success since their implementation, reflecting positive results primarily in the accelerated pace of building a safe and healthy society by reducing the consumption of harmful goods.
Year 2018 had been major for UAE. It saw the entry of Value Added Tax, impacting the country in a whole new way!United Arab Emirates’s (UAE) most significant tax reform!
VALUE ADDED TAX (VAT)
The UAE government implemented value added tax (VAT) in the country from January 1, 2018 at a standard rate of 5%.
VAT has begun to provide the UAE with a new source of income. It has also aided government to move towards its vision of reducing dependence on oil and other hydrocarbons as a source of revenue.
VAT applies equally on tax-registered businesses managed on the UAE mainland and in the free zones. However, if the UAE Cabinet defines a certain free zone as a ‘designated zone’, it must be treated as outside the UAE for tax purposes. The transfer of goods between designated zones are tax-free for certain transactions.
If a person is resident in the UAE, he would be required to get registered for VAT mandatorily if the total value of their taxable supplies and imports made within the UAE exceeds the Mandatory Registration Threshold of AED 375,000 over the previous 12-month period or if the person anticipates that the total value of their taxable supplies or imports will exceed AED 375,000 in the next 30 days.
There is also an option to businesses to get registered for UAE VAT Voluntarily, if at the end of any month, the total value of the person’s taxable supplies and imports or their expenses which were subject to VAT, in the previous 12 months exceeds the Voluntary Registration Threshold of AED 187,500, or the total value of the person’s taxable supplies and imports or their expenses which are subject to VAT, in the next 30 days is expected to exceed the Voluntary Registration Threshold of AED 187,500.
Taxable businesses must file VAT returns with FTA on a regular basis and usually within 28 days of the end of the ‘tax period’ as defined for each type of business. The standard tax period in UAE is quarterly for businesses with an annual turnover below AED150 million and monthly for businesses with an annual turnover of AED150 million or more.The FTA may, at its choice, assign a different tax period for certain type of businesses.
IMPLICATION OF VAT
VAT, as a general consumption tax, applies to the majority of transactions in goods and services.
With 5% of VAT, UAE was anticipatinga major increase in cost of living and thereby affecting purchasing power of consumers in UAE.
In the year 2018, The UAE collected Dh27 billion through VAT revenues, surpassing its target of Dh12 billion.When on one hand VAT implementation has benefited the UAE government in overcoming the budget deficits caused due to declining oil prices which resulted in low revenues in UAE, on the other hand the impact on consumers are varying.
There are basically three categories of VAT Rates in UAE – When the tax treatment of financial services, residential buildings (subject to conditions), bare land and local passenger transport services are exempt; there is another big list under zero rated category. The export of goods, export of services, export of telecommunication services, certain means of transport, international transportation of services for passengers and goods, residential buildings (Subject to conditions), Education services and Healthcare services.All other supplies which are not exempt or zero rates are subject to VAT Standard Rate of 5%.
Generally, a 5% VAT may be hardly noticed by consumers in the UAE, especially as certain food items, essential medical healthcare and education are exempted but there are many households and lower income workers who will feel the need to rethink on the spending. See it from the right angle, you see that the VAT implementation has promoted Tax compliance and also helped in promotion of savings and investment by consumers.
The direct impact on it will vary depending on an individual’s lifestyle and spending behavior. If an individual spends mainly on those things which are relieved from VAT, he is unlikely to see any significant increase.
EVOLUTION OF VAT IN UAE
The introduction of VAT has been under discussion in theGCC since 2004. However, with depleting oil revenuesover recent years, these discussions gathered pacein 2015.
In 2017, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries agreed and announced the first ever Value Added Tax (VAT) framework to allow member nations to develop legislation to start a 5% VAT rate in their respective countries.
It is worth noting that the GCC VAT system is a hybridbased on a combination of both the EU VAT system andthe more recent Goods and Services Tax (GST) systemsimplemented in some Southeast Asian countries.
The UAE ratified the GCC VAT Agreement in May 2017and became the second country to submit its ratification documents to the GCC after the KSA, bringing into force the GCC VAT Agreement.
The Country issued the TaxProcedures Law in July 2017 and the executive regulations on tax procedures in September 2017 establishing a procedural framework for the introduction of Federal taxes in the UAE. The UAE issued its VAT Law and executive regulations in late August 2017 and November 2017, respectively. The effective date of both the UAE VAT Law and executive regulations was 1 January 2018.
The UAE VAT legislation contains transitional rules under which a GCC country would only be recognized as an implementing state if that GCC country treats the UAE as an implementing state and has fully complied with the provisions of the GCC VAT Agreement. Therefore, a GCC country that does not meet these conditions will not be regarded as an implementing state for UAE VAT purposes even if it has introduced VAT under its domestic legislation. A consequence of being a non-implementing state is that the country is treated in the same way as a country outside the GCC.
The UAE’s Federal Tax Authority (FTA) published a number of new and updated guidance documents towards the end of 2019 which clarified the application of some of the existing rules. The FTA intended to further develop its electronic systems for the monitoring, collection and payment of VAT throughout 2020.
NUMBER OF GUIDES, REFERANCES AND PUBLIC CLARIFICATIONS

The Federal Tax Authority adheres to international best practices to ensure that all tax legislations and procedures are implemented thoroughly. All mutual obligations between the Authority and Taxable Persons have been clearly outlined in regulations, which seek, first and foremost, to protect consumers and tighten controls on UAE markets to ensure governance and transparency.
The Authority has held numerous training courses for inspectors at Departments of Economic Development, as well as customs employees in all seven emirates, to ensure that the tax system is implemented smoothly and in a manner that achieves the system’s objectives. The Authority conducted various campaigns which were carried out within the framework of the Authority’s extensive efforts to contribute towards strengthening market performance and ensuring compliance with all tax legislation and procedures to protect legitimate trade and prevent the sale of contraband within the UAE and tax evasion.
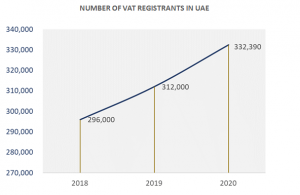
Within 500 days of successful implementation of VAT in UAE, UAE’s tax system has earned praise from experts and official entities in the UAE. During 2020, the Authority maintained increased results, with preliminary statistics showing that the number of registrants for VAT increased to 332,390 registrants, growth of 6.54% of business and Tax Groups and its members, compared to about 312,000 registrants at the end of 2019 and 296,000 registrants at the end of 2018 (the first year of VAT). The Authority successfully processed AED 336.44 million refunded to UAE Nationals based on 4,835 Homebuilder Tax Refund Requests.
Statistics also show that the base of customer and partners benefiting from the tax systems has been steadily expanding, the number of FTA Accredited Tax Agents in the tax system saw steady expansion with the number increasing to 393 compared to 355 at the end of 2019 and 176 at the end of 2018. In addition, the number of FTA approved clearing companies increased to 868 from 122 at the end of 2018, while the number of certified tax accounting system providers jumped to 76 from 12 at the end of 2018.
During 2020, the Authority provided various facilities to support registrants in the tax system to fulfill their tax obligations and ensure business continuity under the precautionary measures put in place by the UAE to prevent the spread of Covid-19. These facilities included the temporary extension of the tax period commencing on the 1st of March for Excise Tax Registrants to cover both March and April 2020. VAT was temporarily applied at the zero-rate on some personal protective medical equipment, such as masks and other items.
VAT IN GCC
When VAT in UAE, is getting big and better with each passing day, lets also see where is UAE and other GCC Countries standing. Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has seen a leap in the VAT Rate from 5% to 15%. The increase came as a part of additional measures taken by the country in response to the economic impact of the Covid-19 crisis. Bahrain having implemented VAT with effect from 1st January 2019, is continuing to issue new sector and topic-specific VAT guidance, to provide support and clarity to businesses operating in the state. Qatar imposes no VAT or sales tax on operations in Qatar. However, the introduction of VAT in Qatar under a common GCC framework is expected to be introduced in the near future with an anticipated tax rate of 5%. The tax authorities in Kuwait recently announced that it will finally introduce Value Added Tax (VAT) at 5% from 1 April 2021. Oman is set to be the fourth GCC state to implement VAT since the signing of the GCC VAT Agreement at the end of 2016, with an effective date of 16 April 2021. The Oman VAT Law was published in the official gazette on 18 October, This triggered a 180-day countdown to the effective date of 16 April 2021.
SOME KEY FEATURES OF UAE VAT
- VAT Refund for tourists:
VAT refund for Tourists are carried out through a fully integrated electronic system which connects retailers registered in the ‘Tax Refund for Tourists Scheme’ with all ports of entry and exit from the UAE.
“Planet” is the exclusive operator of the tax refund system for tourists which the Federal Tax Authority executes in the UAE. The tourist however, should have met certain conditions laid by the authority specifically to claim the VAT Refund.
Tourists will receive their refunds through a special device placed at the departure port – airport, seaport, or border port – by submitting the tax invoices for their purchases from the outlets registered in the Scheme, along with copies of their passport and credit card.
Once these documents are submitted, tourists can either recover the VAT in cash in UAE dirhams, or have it transferred to their credit card.
- Foreign Business Refunds
The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) does allow the foreign companies to claim back Value Added Tax (VAT) incurred while doing business in the UAE.
To be eligible for the VAT refund, the first condition is that foreign businesses must not have a place of establishment or fixed establishment in the UAE or in any of the VAT-Implementing GCC States that fully comply with the provisions of the Common VAT Agreement of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf. Such foreign businesses must not be a Taxable Person in the UAE. They must also be registered as an establishment with a competent authority in the jurisdiction in which they are established.And finally, they must be from a country that implements VAT and that equally provides VAT refunds to UAE businesses in similar circumstances.
3. UAE Designated Free Zones
UAE has specified areastermed as “Free Zones”, which are considered different from the UAE Main Land.
Historically, Free Zones have been excluded from the territorial scope of the UAE. However, for VAT purposes, this is not automatically the case. Only those Free Zones listed in a Cabinet Decision qualify for special VAT treatment and that special VAT treatment has certain limitations. These nominated Free Zones are known as Designated Zones for VAT purposes.
The effect for businesses operating in Designated Zones will be that many supplies of goods will be outside the scope of UAE VAT, subject to strict criteria and detailed record keeping. However, supplies of services are subject to the normal UAE VAT rules.
ANTICIPATION, EXPECTATIONS AND DEVELOPMENTS
As Covid hit, there was an anticipation that UAE would declare an increased rate of VAT. The panic was put down with an announcement by the Ministry during May 2020. The Ministry of Finance (MoF) denied any plans to raise the Value Added Tax (VAT) in the United Arab Emirates. VAT is currently levied at 5%, and the announcement reaffirmed the ministry’s commitment to achieve the country’s development goals and plans.
In the context of keenness to continuously develop the Authority’s official payment channels and encourage the use of electronic payment methods, the year 2020 saw the FTA’s accession to the third generation of the e-Dirham system with its diverse channels launched by the UAE Ministry of Finance to allow the efficient collection of fees and revenues of the UAE, and provide more options for the payment of such government fees by using the latest technologies underpinned by the best safety standards
The Federal Tax Authority, through its innovation strategy, is seeking to be a global leader by applying innovative mechanisms to implement tax-related procedures and collect taxes. The FTA’s three initiatives included the ‘Tax Innovation Lab’ initiative, which involves holding remote brainstorming meetings on various critical topics that promote innovative ideas, the second initiative, ‘Monitoring Tax Innovations’, highlighted the most remarkable innovative achievements in the tax field, and the third initiative was a series of online comprehensive talks, comprised of virtual dialogue sessions on innovation management, research and development and future trends in the field.
CONCLUSION
VAT in UAE brought with it the transparency and accountability, which has contributed to increasing the global competitiveness, and it has benefited the business among the regional market.Introduction of VAT required businesses to maintain proper books and this discipline has helped businesses to understand, analyze, and control their business performance better, and ensure ongoing VAT compliance.
The high compliance ratio and awareness campaigns by the Federal Tax Authority had been remarkable. Along with that, new regulations has made its appearance – such as economic substance, country-by-country reporting and BEPS (base erosion and profit shifting). Having all of these collectively, compliance is definitely going to be the most sorted after objective of the country. We have also seen recently, how The Federal Supreme Court in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has released a long awaited decision in favour of Federal Tax Authority’s policy with regard to penalty applied. This has definitely put light on the commitment that is demanded in the tax compliance.
The taxation system has been and will be unfolding broad and wide with time!



